Parts of a Plant: Nature is a beautiful creation of the Almighty. It is surrounded by plants and other such natural elements, which are important for our knowledge. Hence, we have penned down this article so that learners have no trouble in solving parts of the plant worksheet, with the help of our parts of plants and their functions, list.
This list of Plant Parts will aid learners in memorizing this information with parts of a plant diagram.
Study the most important English Vocabulary Words identified by our experts and learn the right vocabulary to use in your day to day conversations
List of Plant Parts
Name of Plant Parts
Description of Plant Parts
List of a Plant Body
The berry in most plants is a simple fruit which has a fleshy and juicy interior and consists of a thin outer cover. Most wild plants have berries which turn from green to reddish when ripe.
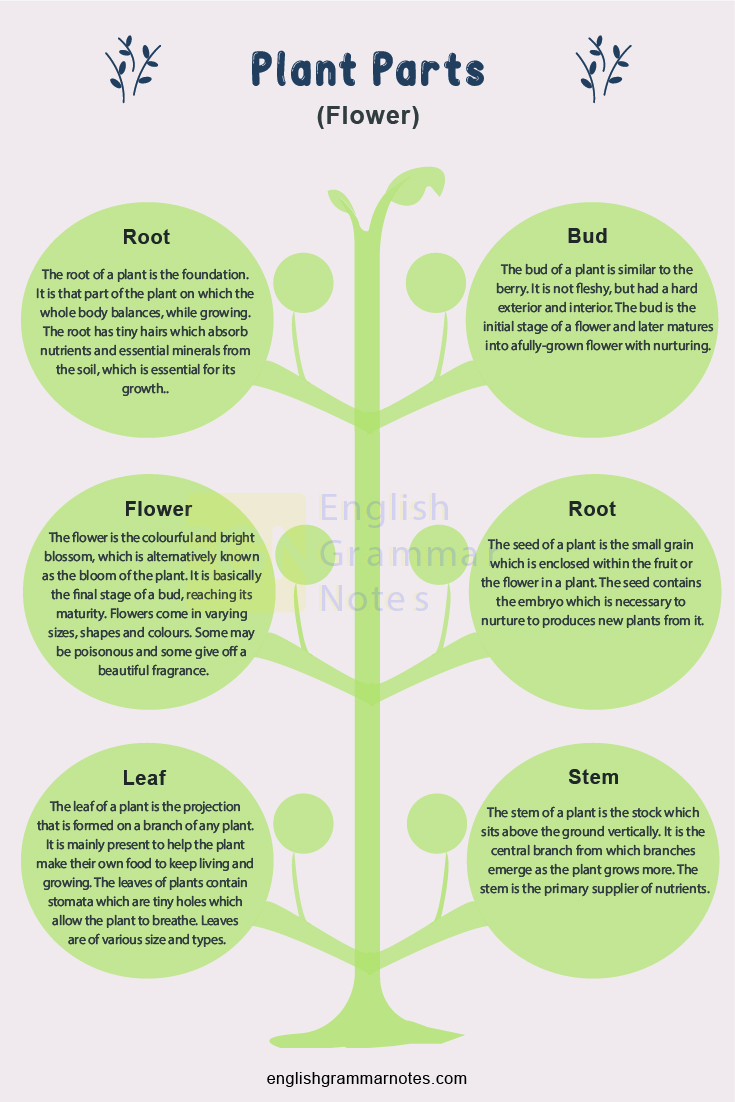
The root of a plant is the foundation. It is that part of the plant on which the whole body balances, while growing. The root has tiny hairs which absorb nutrients and essential minerals from the soil, which is essential for its growth.
The bud of a plant is similar to the berry. It is not fleshy, but had a hard exterior and interior. The bud is the initial stage of a flower and later matures into a fully-grown flower with nurturing.
The flower is the colourful and bright blossom, which is alternatively known as the bloom of the plant. It is basically the final stage of a bud, reaching its maturity. Flowers come in varying sizes, shapes and colours. Some may be poisonous and some give off a beautiful fragrance.
The leaf of a plant is the projection that is formed on a branch of any plant. It is mainly present to help the plant make their own food to keep living and growing. The leaves of plants contain stomata which are tiny holes which allow the plant to breathe. Leaves are of various size and types.
The seed of a plant is the small grain which is enclosed within the fruit or the flower in a plant. The seed contains the embryo which is necessary to nurture to produces new plants from it.
The sprout is the time or a feature in plants when a new bud is growing on the tip of a branch. The more the sprouts the more flowers the plant has.
The stem of a plant is the stock which sits above the ground vertically. It is the central branch from which branches emerge as the plant grows more. The stem is the primary supplier of nutrients.
Parts of a Flower
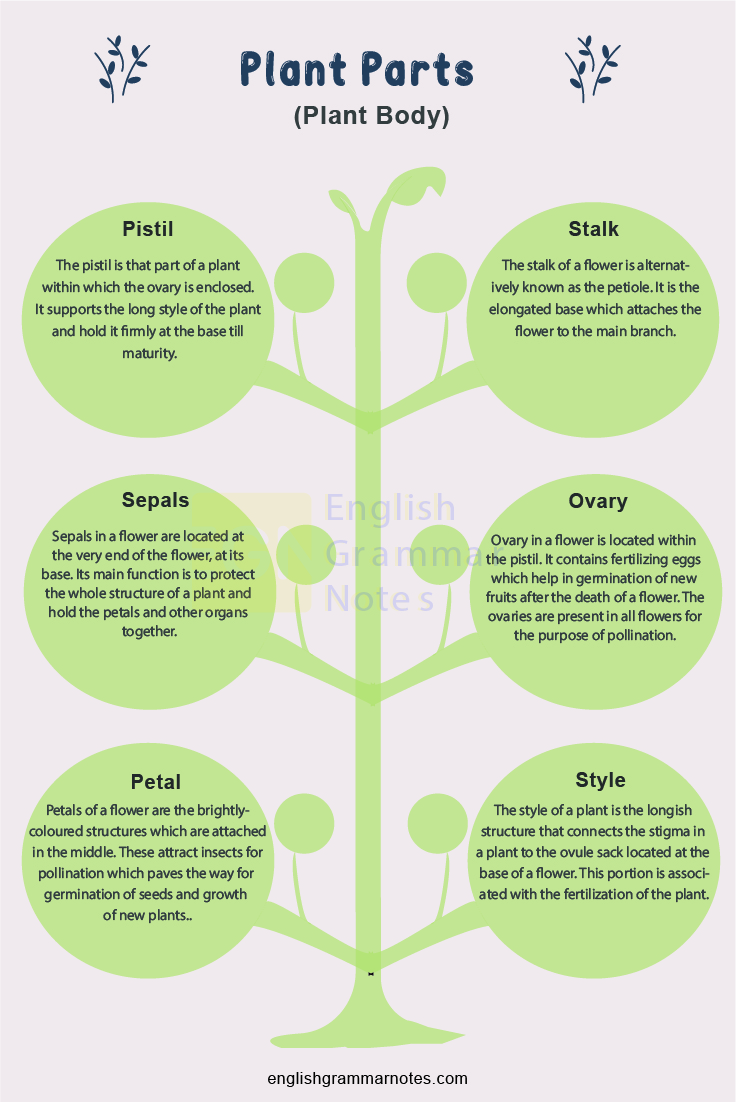
Petals of a flower are the brightly-coloured structures which are attached in the middle. These attract insects for pollination which paves the way for germination of seeds and growth of new plants.
The pistil is that part of a plant within which the ovary is enclosed. It supports the long style of the plant and hold it firmly at the base till maturity.
The style of a plant is the longish structure that connects the stigma in a plant to the ovule sack located at the base of a flower. This portion is associated with the fertilization of the plant.
Ovary in a flower is located within the pistil. It contains fertilizing eggs which help in germination of new fruits after the death of a flower. The ovaries are present in all flowers for the purpose of pollination.
Pollen grains are dusty minute particles attached to the anther of a flower. It acts as the main source initiating in the pollination of a plant. These pollen grains stick to the bodies of pollinating agents like bees, butterflies, moths (any such nectar-consuming insect) and get transmitted to male plants, making pollination possible.
Sepals in a flower are located at the very end of the flower, at its base. Its main function is to protect the whole structure of a plant and hold the petals and other organs together.
The stalk of a flower is alternatively known as the petiole. It is the elongated base that attaches the flower to the main branch.
The stigma is the specially modified portion of a flower pistil that sits upright within the flower to ensure pollination. It is slender-built and has a sticky surface which helps the pollen from the body of vectors, stick to them and help in carrying out, the process of pollination.
Parts of a Tree
The bark of a tree is the outer layer or covering of the branch and trunk of the tree. It is rugged and sturdy, helping the plant withstand rough weather and wind.
The branch of a tree is the elongated projections that emerge from the main stem of the plant or the trunk. They are tough and make up most of the canopy in trees.
Leaves of the tree are units of transpiration in plants. They help the plant to release oxygen and intake carbon di oxide, and produce their own food with the help of cellulose.
Flowers are the attractive and colourful, pollen-producing part of a plant. They attract vectors or insects for pollination and maintain the overall aesthetic in plants.
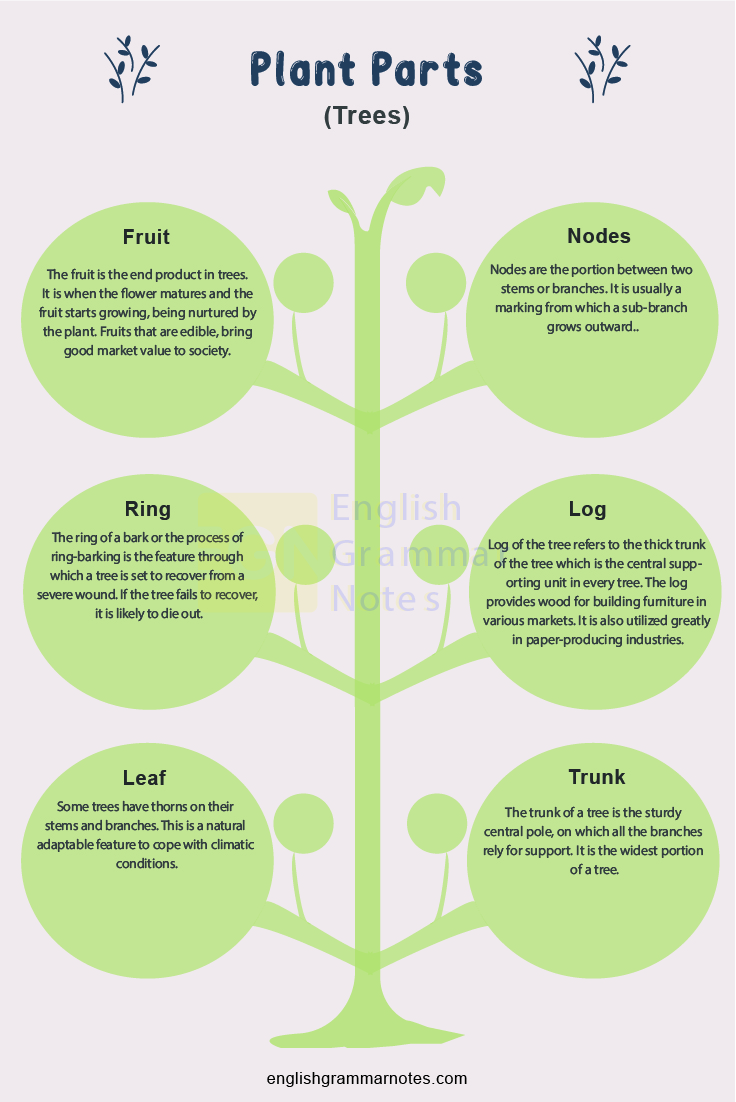
The fruit is the end product in trees. It is when the flower matures and the fruit starts growing, being nurtured by the plant. Fruits that are edible, bring good market value to society.
Nodes are the portion between two stems or branches. It is usually a marking from which a sub-branch grows outward.
Log of the tree refers to the thick trunk of the tree which is the central supporting unit in every tree. The log provides wood for building furniture in various markets. It is also utilized greatly in paper-producing industries.
The ring of a bark or the process of ring-barking is the feature through which a tree is set to recover from a severe wound. If the tree fails to recover, it is likely to die out.
The roots of a tree ate the main section which absorb minerals and water from the soil, helping in the nurturing of the tree.
Some trees have thorns on their stems and branches. This is a natural adaptable feature to cope with climatic conditions.
The trunk of a tree is the sturdy central pole, on which all the branches rely for support. It is the widest portion of a tree.