Parts of the Mouth Vocabulary: In the anatomy of humans, the first portion of the alimentary canal which produces saliva and receives the food is the mouth.
Our mouth plays an important role in communication and, on top having the primary role of the beginning of the digestive system. The throat, the tongue, the lips, and the jaw are some of the most important mouth parts name.
For you to know about the mouth parts name in English, we have made a list of parts of the mouth vocabulary words.
Study the most important English Vocabulary Words identified by our experts and learn the right vocabulary to use in your day to day conversations
List of Parts of Mouth Vocabulary Words in English
Name of Parts of mouth Vocabulary Words
Our mouth consists of two regions, the oral cavity proper, and the vestibule. The area between the teeth, the lips, and the cheeks is the vestibule. Our mouth, which is normally moist, is covered with the mucous membrane, and it consists of teeth. The start of the mucous membrane, which covers the rest of the body, is marked by the lips which forms an integral part of the mouth parts diagram.
List of Parts of Mouth
Description of the Parts of Mouth Vocabulary Words
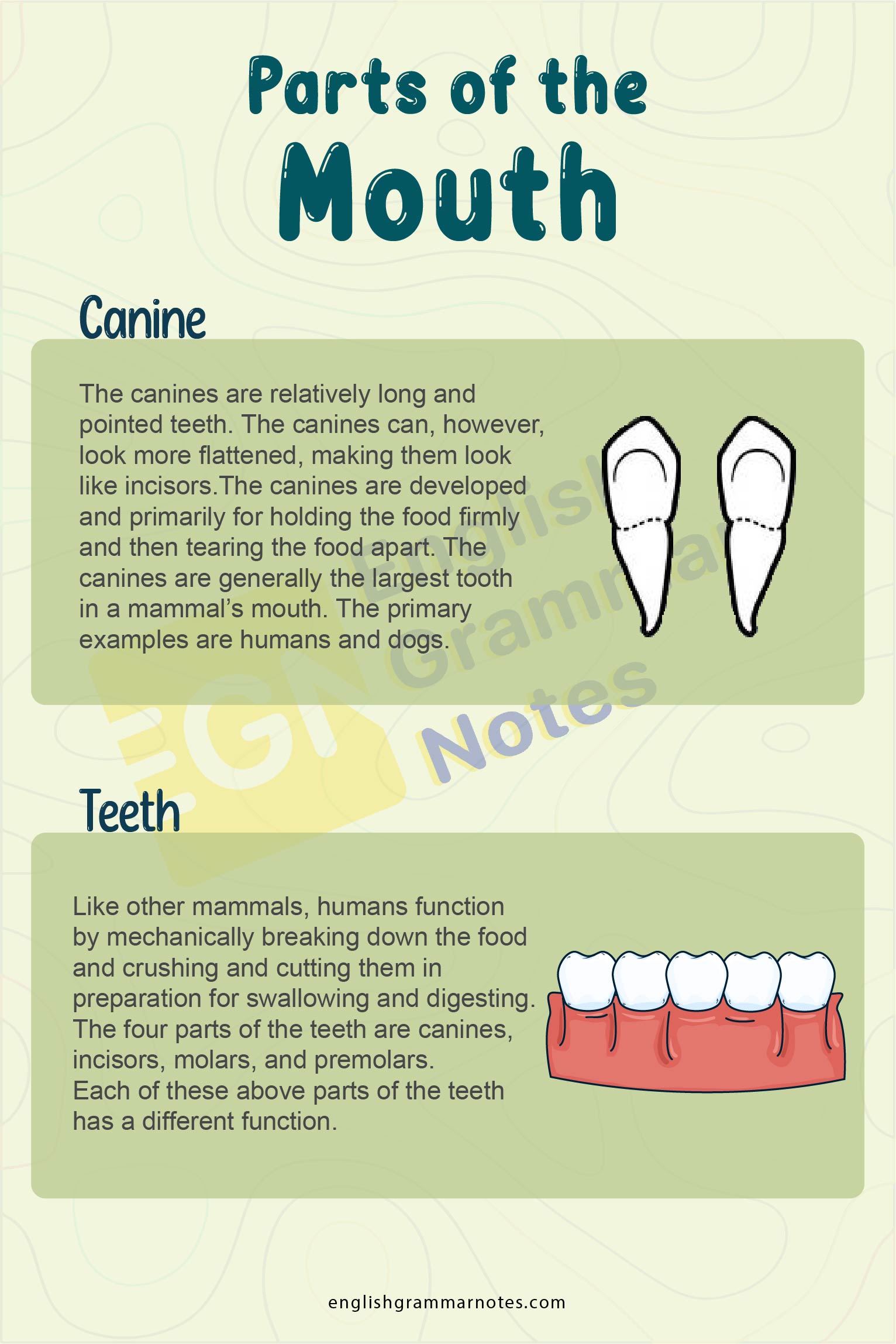
Canine
In the oral anatomy of mammals, canines are also known as the dog teeth, the cuspids, the vampire teeth, or vampire fangs. The canines are relatively long and pointed teeth. The canines can, however, look more flattened, making them look like incisors.
The canines are developed and primarily for holding the food firmly and then tearing the food apart. The canines are generally the largest tooth in a mammal’s mouth. Individuals mostly develop four canines, two in the upper jaw and the two in the lower jaw, separated by incisors in each jaw. The primary examples are humans and dogs.
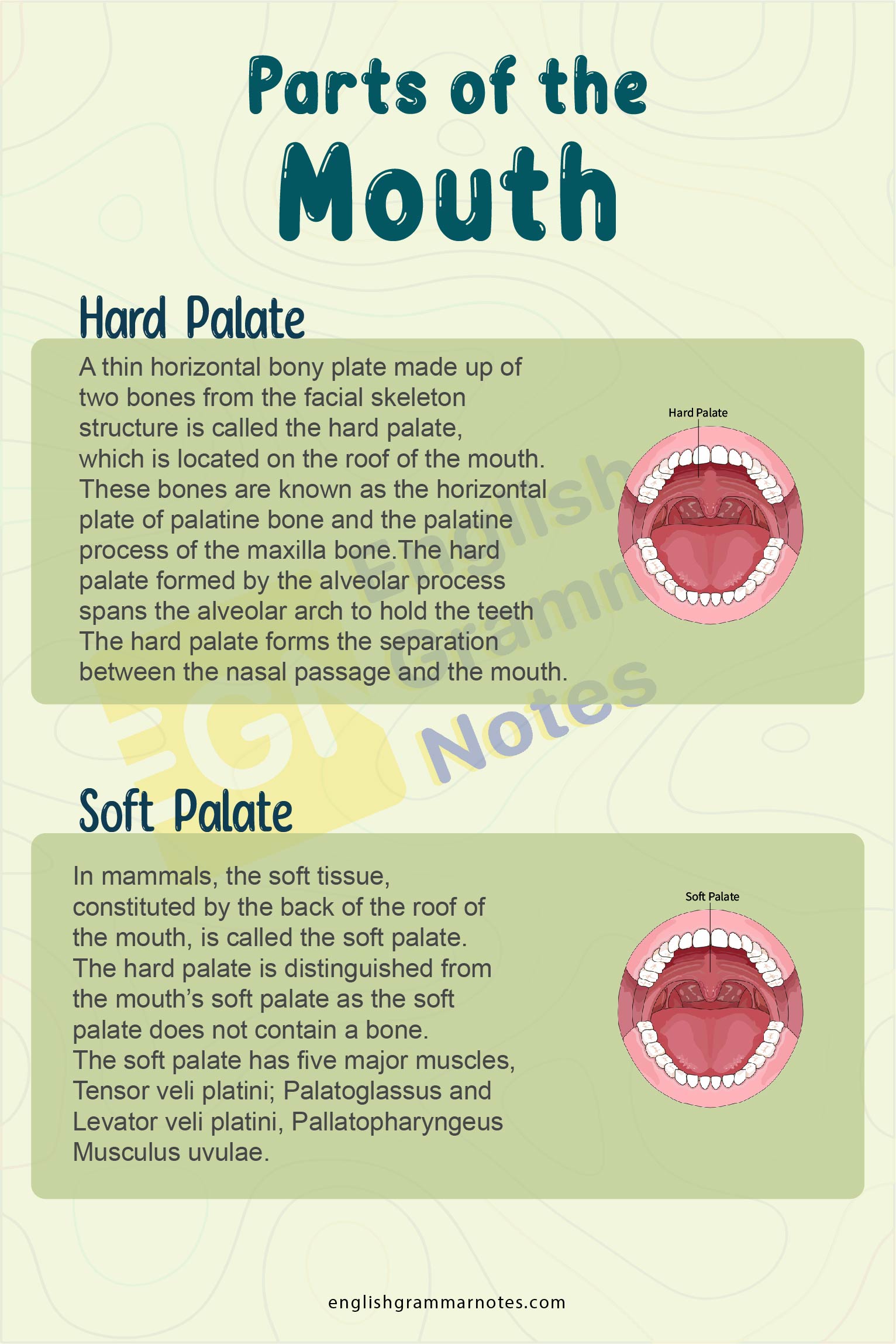
Hard Palate
A thin horizontal bony plate made up of two bones from the facial skeleton structure is called the hard palate, which is located on the roof of the mouth. These bones are known as the horizontal plate of palatine bone and the palatine process of the maxilla bone.
The hard palate formed by the alveolar process spans the alveolar arch to hold the teeth. The hard palate forms the separation between the nasal passage and the mouth. The irregular ridges in the mucous membrane help facilitate the movement of the food in the mouth and the plicae in the interior portion of the mouth.
Soft Palate
In mammals, the soft tissue, constituted by the back of the roof of the mouth, is called the soft palate. The hard palate is distinguished from the mouth’s soft palate as the soft palate does not contain a bone.
The soft palate has five major muscles, which helps and play important roles in breathing and swallowing food. Those muscles are:-
- Tensor veli platini; this muscle is involved with the role of swallowing the food.
- Palatoglassus and Levator veli platini, these two muscles are also involved in swallowing
- Pallatopharyngeus is a muscle that helps in breathing
- Musculus uvulae, this muscle helps to move the uvula.
Lips
All mammals, including humans, lips are a visible body part of the mouth, and they are soft and movable. Lips help with sound and speech, and they serve as an opening for food intake.
Labium Superius Oris is referred to as the upper lip, and Labium Inferius Oris is referred to as the lower lip. The juncture where the surrounding lip area meets the lips is called the vermilion border. The vermilion lining of the upper lip is widely recognized as the Cupid’s Bow.
As compared to the facial skin, the skin of the lip have four to five layers, whereas the facial skin has fifteen to sixteen layers. A lip skin does not have sweat glands and is not hairy. This is the reason why our lips tend to get dry more easily and get chapped frequently in winters.
Uvula
The uvula, also known as the palatine uvula, is the middle of the soft palate, which is a conic projection from the back edge. This soft palate consists of a number of racemose glands and the connective tissue of the palate and the uvula. The uvula also consists of a lot of senous glands which produce thin saliva.
The uvula muscular part broadens and shortens the muscle. The posterior part of the soft palate changes the contour. They prevent the food which we intake from entering the nasal cavity during swallowing, the soft palate, and the uvula close together from bringing and closing off the nasopharynx.
Tongue
The tongue is a typical vertebrate in the muscular part of the mouth. As a part of the digestive process, it manipulates food for swallowing and mastification. The upper surface of the tongue is covered by numerous lingual papillae and taste buds. Our tongue also serves the purpose of cleaning our teeth naturally.
Our tongue is divided into three different parts, at the front, the oral part, and a pharyngeal part at the back. By its length, the left and ride side is also separated by a fibrous tissue which results in the median sulcus and the groove on the tongue’s surface.
There are two different muscles of the human tongue. The four muscles, which are intrinsic, alter the shape of the tongue and are not attached to any bone. At the same time, the extrinsic four tongue muscles are anchored to the bone and change the position of the tongue.

Gingiva
Inside the mouth, the mucosal tissue that lies over the Mandible and maxilla is called the gingiva or the gums. General health can have effects if our gum health is weak or if we have any gum disease.
The gingiva or the gums are a part of the soft lining tissue of a mouth. They provide a seal to the teeth and surround them. Most of the gums, unlike the soft lining tissue of the cheeks and lips, are tightly bound to an underlying bone which prevents the food from passing over them and resists the friction.
Coral pink in lightly skinned people indicated healthy gums, whereas some gums are maybe naturally darker with the pigmentation of melanin.
Incisor
The teeth in the front, which are present in most mammals, are called the incisors ( in Latin: to cut). They are located below the Mandible and above the premaxilla. A total of eight incisors are found in the human mouth.
Adult humans develop up to eight incisors. Those are mentioned below:-
- Maxillary central incisor which is found near the closest center of the lips and the upper jaw
- Maxillary lateral incisor is found beside the maxillary central incisor and the upper jaw
- Mandibular lateral incisor is situated beside the mandibular central incisor in the lower jaw
- Mandibular central incisor is found closest to the center of the lips and the lower jaw
Papillae
The small nipple-like structures which are present on the roof of the tongue are called papillae. The papillae give the roof of the tongue a rough texture. Papillae can be more easily seen in mammals when the tongue is dry.
There are four forms of papillae.
Mandible
In the human facial skeleton, the Mandible, jaw, or the jawbone, is the lowest and the strongest bone. It strongly holds the lower teeth in place and forms the lower jaw. The temporomandibular bones and the temporal bones are connected. The one and only movable bone in the skull is the Mandible.
The mandible word is derived from the Latin word mandibula. Mandere means chew and bula, which is an instrumental suffix.
Teeth
Like other mammals, humans function by mechanically breaking down the food and crushing and cutting them in preparation for swallowing and digesting. The four parts of the teeth are canines, incisors, molars, and premolars.
Each of these above parts of the teeth has a different function. The incisors are mainly functional for cutting the food, the canines are used to tear the food, and the molars and the premolars are for crushing the food.
Premolar
The transitional teeth between the canine and the molar teeth, the bicuspids, are also called the premolar teeth. There are eight premolars in the mouth in total, and there are two premolars per quadrant in the permanent set of teeth. During chewing or mastication, the premolars are considered transitional teeth.
There are four types of premolars in the human mouth. Those are:-
- Maxillary first premolar
- Maxillary second premolar
- Mandibular first premolar
- Mandibular second premolar